What is Eczema
Eczema infection refers to a skin condition characterized by red, elevated, bumpy patches of skin associated with itching and dryness of the skin.
Eczema-prone skin is more susceptible to bacterial and fungal infections due to its compromised barrier function.
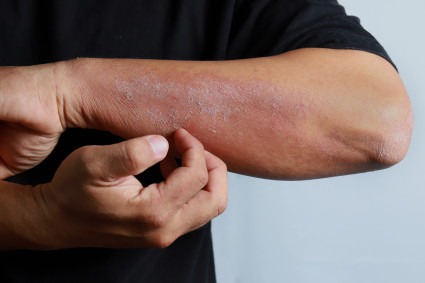
Eczema is a common skin condition. It affects people with dry and sensitive skin. The affected area is red and inflamed. Moreover, it can blister or crack. The protective oily or ‘lipid’ layer of skin seals in the moisture of the skin. Sometimes, this layer degrades. As a result, the skin loses its moisture. Therefore, this makes the skin flaky and prone to develop eczema.
Moreover, eczema infection can also be an allergic reaction to food, pollen, soaps, perfumes, and medications, which can act as triggers. Moreover, heredity, immune disorders, and stress can also be one of the causes of eczema infection.
Struggling with the discomfort of eczema? Say goodbye to itchiness and irritation by exploring the best eczema treatments available. Our leading dermatologist in Pune is at the forefront of providing effective, personalized solutions for this challenging skin condition.
Don’t let eczema control your life. Book an appointment at Pune’s top skin care clinics and consult with our expert dermatologists. Call +919584584111 now and start your journey towards healthier, more comfortable skin under the care of Pune’s finest skin specialists.
Table of Content
Do & Don’t for Getting Eczema
Grades of Eczema
Different Types: Eczema Infection
Causes of Eczema Infection in Adults
Causes of Eczema in Children
Treatment for Eczema
Do & Don’t for Getting Eczema
DO: Check product labels for ingredients that suit you.
DO: Moisturize regularly.
DO: Stay hydrated.
DO: Stay stress-free.
DON’T: Don’t use scented products.
DON’T: Bath for too long with very hot water.
DON’T: Don’t Scratch the affected area.
Grades of Eczema
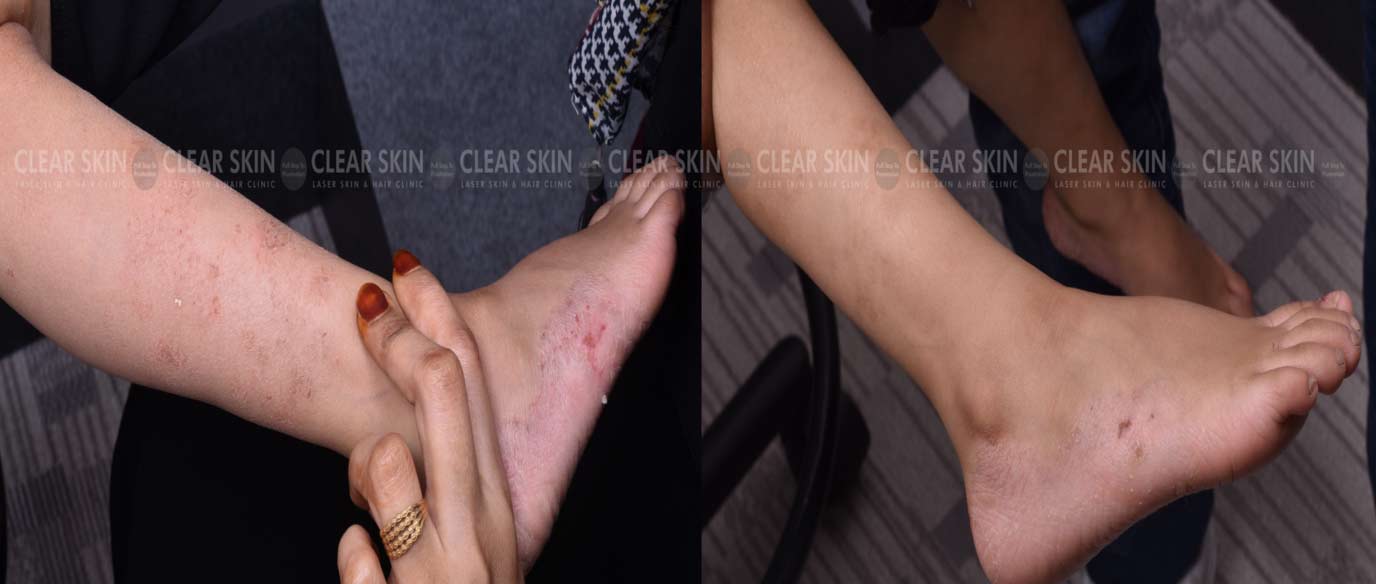
- Acute eczema infection is an early stage of eczema. It is a rapid onset of reddened and inflamed eczema flares. Sometimes small fluid-filled blisters or oozing can also present.
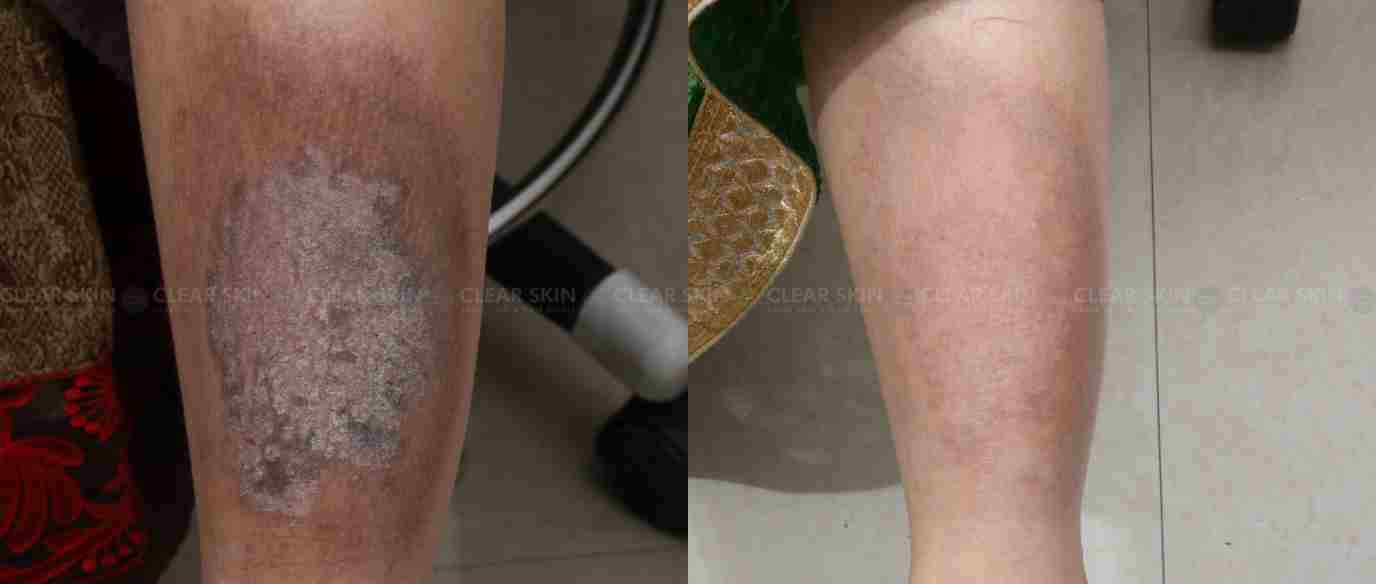
- Chronic eczema is eczema lasting for more than 6 weeks. In this, the lesion becomes dark in color and thickened.
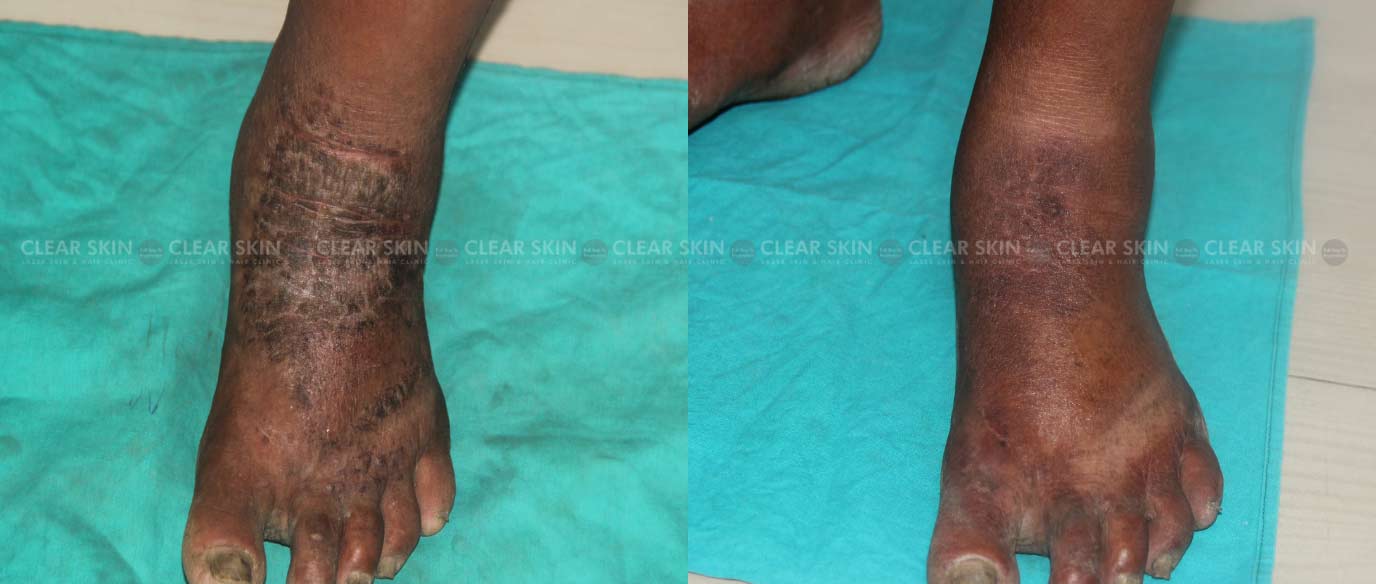
- Infected eczema is an eczema with a secondary infection. It can be associated with pain, redness, swelling in surrounding skin, and sometimes pus-filled blisters.
Different Types: Eczema Infection
- Atopic eczema infection: It occurs due to genetic and environmental factors associated with an immune response. It is seen commonly in children but can also affect adults. There is generalized dry skin with itching mainly in body folds.
- Discoid eczema infection: It appears as discrete coin-shaped itchy areas or islands of skin on a background of normal or dry skin.
- Allergic contact eczema infection: It occurs due to long-standing contact with something which sensitizes the skin, producing allergic eczema. Eg.- metals, cosmetic products, and detergents.
- Irritant contact eczema infection: It occurs immediately or within a short time after contact with the culprit agent. in this burning sensation, redness and blisters develop in the area of contact.
- Dyshidrotic eczema: It occurs on areas of the body that sweat, especially hands and feet in the form of itchy blisters.
- Neurodermatitis: It starts with an itchy patch of skin that becomes itchier if scratched and eventually becomes long-standing, the thickened plaque with intense itching
- Seborrheic eczema infection: It occurs due to increased secretion of sebum associated with inflammation. Which causes reddish, oily, scaly patches on the scalp, some areas of the face such as the nasolabial fold, eyebrows, and beard in males, behind ears, and upper chest.
- Stasis dermatitis: It occurs because of conditions causing improper circulation of blood such as varicose veins., and is commonly seen on the lower legs.
Causes of Eczema infection in Adults
- Irritants like soaps, shampoos or bubble baths, and exfoliating scrubs can cause eczema in adults.
- Environmental factors or substances causing allergies can lead to eczema in adults. These include cold, dry weather, dampness in the air, and even pollen, dust mites, and pet fur.
- Stress is another leading cause of eczema.
- Hormonal changes in women can trigger eczema in them.
- Certain skin conditions like atopic dermatitis can lead to eczema flare-ups in adults.
- Certain fragrances can cause eczema, which means scented products can trigger this skin condition.
- Rough fabrics can trigger this skin condition in adults and children alike.
Causes of Eczema on Eyelids
- When the eyelids are exposed to allergens or irritants, one can get eyelid eczema. This condition is also called eyelid dermatitis, periocular dermatitis, or periorbital dermatitis.
- Certain skin diseases may have eyelid eczema as a symptom.
- Certain makeup products and soaps can irritate the region around the eyes and the eyelids, thus causing eyelid dermatitis.
Causes of Eczema on the Face
- Cleaning products like soaps and shampoos, scented products, smoke, and makeup products with ingredients like nickel and fabric dyes can cause eczema of the face.
- Pollen, dust, animal dander, and mould are some allergens that can cause facial eczema.
- Stress can lead to facial eczema
- Makeup products can cause dryness.
- Hormonal fluctuations are another common cause of eczema on the face.
Causes of Eczema on Hands
- Frequently wet hands are one of the causes of hand eczema, also called hand dermatitis.
- Irritants like dust, soaps, detergents, or certain sprays can cause eczema on the hands.
- Excessive hand washing is another important cause of eczema on hands.
- Dry air and sudden temperature changes in winter can lead to hand eczema.
- Certain chemicals, rubber, and some plants can lead to hand eczema.
Causes of Eczema in Children
- The causes of eczema in adults, which are enlisted above, also apply to children.
- It has been found that many children with eczema do not have adequate levels of a protein called filaggrin which is present in the upper layer of the skin. This protein helps form a barrier between the skin and the environment. Due to the lack of this protein, the skin finds it difficult to retain moisture and also prevents bacteria from entering the skin.
- Food allergies are a leading cause of eczema in children.
- Kids and teenagers who have eczema often have a family history of this skin condition.
If you want to know how to get clear skin after eczema, it is best to consult a dermatologist. He would guide you well regarding which home remedy or treatment method for eczema would suit you best.
Treatment for Eczema
It can recur from time to time to get the best Eczema infection.
To get an instant best eczema treatment, Our expert dermatologists in Pune offer tailored approaches to address the underlying causes of eczema.
There is no cure for Eczema. It can recur from time to time. Therefore, one must keep the triggers of eczema under control. If you suffer from eczema skin problem, you must
- Know your triggers
- Maintain a regular bathing and moisturizing routine
- Be careful of any signs of eczema infection on the skin. These could include pus-filled bumps, pain, or redness.
Despite all these efforts, eczema can still flare. Eczema can be an unpredictable disease. There are multiple treatment modalities for eczema. Most of the treatments are topical, but in severe cases, even oral medicines can be prescribed. These medications should only be taken under prescription as steroidal treatments if not used correctly may cause side effects like skin thinning or stretch marks.
There are several treatment modalities for Eczema:
Moisturizers are one of the most important aspects of managing eczema infection. When your skin is dry, it can get irritated. As a result, eczema can flare. Moreover, wind, low humidity, cold temperatures, harsh soaps, and too much washing without the use of a moisturizer can cause dry skin. It’s important to know how and when to properly moisturize and bathe. In fact, it is important to use only those products which are best to use for eczema.
-
Topical corticosteroid creams and ointments
These are a type of anti-inflammatory medication. They help to relieve skin inflammation and itchiness. One must apply them directly on infected area where eczema on face skin. However, make sure you consult with your dermatologist. Do not use any eczema creams without a dermatologist’s prescription.
Dermatologists may prescribe systemic corticosteroids when topical treatments don’t work and the eczema is severe and extensive. These are oral medications. Moreover, one must use them only for short periods of time and only after a dermatologist’s prescription to prevent any unwanted side effects.
This includes UVA light therapy and UVB therapy. By exposing the affected areas to UV rays, this treatment aims to reduce itching and inflammation and increase defense systems in the skin.
- These are present in topical as well as oral formulations.
- These are mainly used as steroid-sparing agents in patients with long-standing eczema
- topical agents are tacrolimus, pimecrolimus, and vitamin D analogs.
- oral agents like cyclosporine, azathioprine are used very rarely and only with patients with extensive disease.
- Histamine is the substance in the skin that causes itching.
- Antihistamines block the action of histamine and help relieve itching.
- Sedative preparations can also be prescribed to those in whom sleep disturbance because itching is a major symptom of eczema.
Antibiotics are used to treat infected eczemas.
This involves covering the affected affected skin with topical corticosteroids and wet bandages which is done in severe non-responsive eczema, only if recommended by a dermatologist.