- Home /
- Blogs
Skin Central: Your Source For Clear Skin Knowledge
Your Ultimate Destination for Expert Insights on Achieving Clear and Healthy Skin.
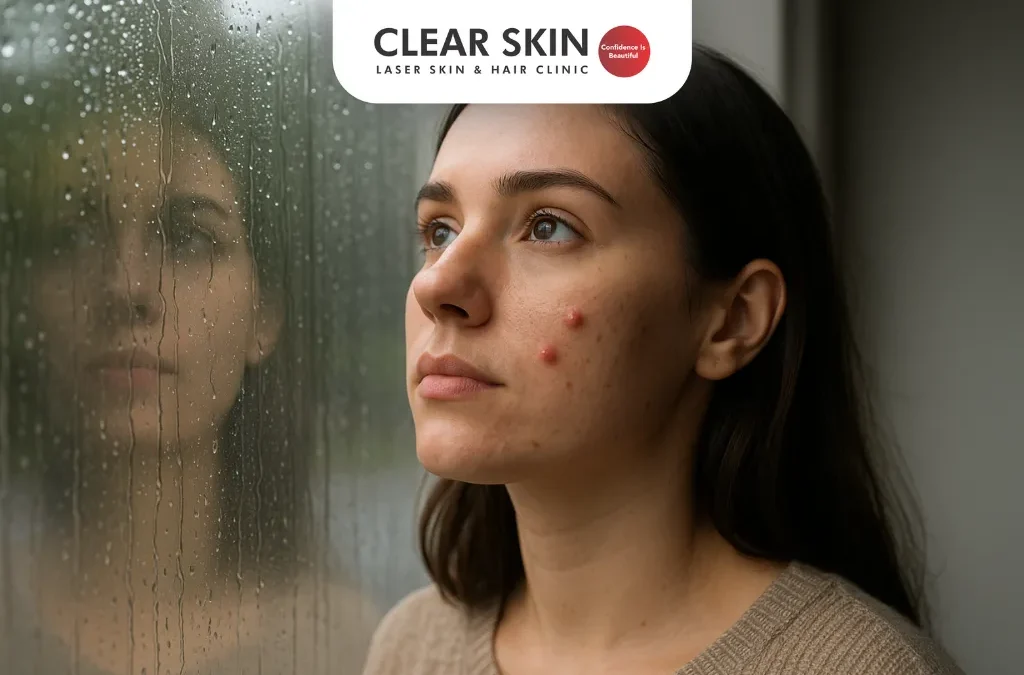

How to Avoid Acne in Monsoons?
Avoid acne in monsoons with a gentle skincare routine, diet tips, and hydration. Get expert advice to manage breakouts and keep your skin clear and healthy.
Does Makeup Cause Acne-Prone Skin?
Worried about breakouts from using makeup? Does makeup cause acne for you? Learn the safe ways to apply makeup for acne-prone skin.
Morning Skin Care Routine for Glowing Skin
Clear Skin Clinic, led by top dermatologists, shares the ideal morning skincare routine to help you achieve a radiant complexion naturally and effectively.
Monsoon Skin Care Tips for Radiant, Healthy Skin
Clear Skin Clinic, led by top dermatologists, shares the ideal morning skincare routine to help you achieve a radiant complexion naturally and effectively.
How To Take Care Of Oily Skin in Monsoon?
Oily skin care in monsoon focuses on gentle cleansing, hydration, and protection to reduce breakouts, greasiness, and help maintain skin balance daily.
Is Laser Hair Removal a Permanent Solution?
Can Laser Treatment Remove Hair Permanently?
Skin Care Tips – Monsoon Skincare Routine to Follow
Protect your skin this monsoon with a dermatologist-approved monsoon skincare routine. Simple steps for hydrated, glowing skin.
Most Comprehensive Patient Guides
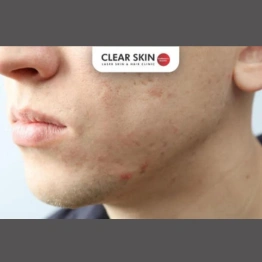
Difference Between Acne And Pimples
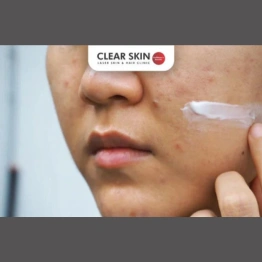
Do Acne Scar Removal Creams Really Work?

How to Reduce Lip Pigmentation: Effective Methods

Powerful Home Remedies for Dark Circles
Dermatologist Insight: Decoding Popular Claims
Grab Your Free E-Book
We are committed not only to treating you, but also educating you.
Most Read Blogs
How Monsoon Affects Your Skin and How to Care for It
Home / Blogs /Monsoon Affects Your Skin and How to Care for It? How Monsoon Affects Your Skin and How to Care for It?Reviewed By: Dr. Dhanraj ChavanUpdated on: 18th june, 2025Rain may soothe your soul, but it can stress your skin — here’s how to fight back.The...
How to Get Clear Skin? | Ultimate Guide with #140 Ways
Home / Blogs / How to Get Clear Skin? | Ultimate Guide with #140 WaysHow to Get Clear Skin? | Ultimate Guide with #140 Ways Reviewed By: Dr. Dhanraj ChavanUpdated on: 06th June, 2025The expert Dermatologists at Clearskin have compiled this ultimate guide for you...
Dos and Don’ts of Skin Hydration | Healthy Skin Tips
Home / Blogs / Dos and Don’ts of Skin HydrationDos and Don’ts of Skin HydrationReviewed By: Dr. Dhanraj ChavanUpdated on: 29th May, 2025Hydrated skin is healthy skin. But are you doing it right, or making mistakes that leave your skin thirsty for more?Hydrated...
Is Sports Equipment Causing Your Acne?
Home / Blogs / Is Sports Equipment Causing Your Acne?Is Sports Equipment Causing Your Acne?Reviewed By: Dr. Dhanraj ChavanUpdated on: 25th May, 2025Sports gear protects your body, but could it be harming your skin?For many athletes and fitness enthusiasts, clear...
How to Treat Dry Skin in the Summer?
Home / Blogs / How to Treat Dry Skin in the Summer?How to Treat Dry Skin in the Summer?Reviewed By: Dr. Dhanraj ChavanUpdated on: 24th May, 2025Dry skin in summer? Yes, it’s a thing. And the good news is—it's easy to treat with the right care.The summer season...
Is Workout Causing Your Acne?
Home / Blogs / Is Your Workout Causing Your Acne?Is Your Workout Causing Your Acne?Reviewed By: Dr. Dhanraj ChavanUpdated on: 23rd May, 2025Working out is great for your body, but it can sometimes lead to pimples on your face, chest, or back. Sweat, dirt, and...
How Aloe Vera Combats Acne and Reveals Radiant Skin?
Home / Blogs / How Aloe Vera Combats Acne and Reveals Radiant Skin?How Aloe Vera Combats Acne and Reveals Radiant Skin?Reviewed By: Dr. Dhanraj ChavanUpdated on: 20th May, 2025Discover how aloe vera helps fight acne and gives you clear, glowing skin with its...
How to Get Clear Skin?
Home / Blogs / How to Get Clear Skin? How to Get Clear Skin?Reviewed By: Dr. Dhanraj ChavanUpdated on: 19th May, 2025The expert Dermatologists at Clearskin have compiled this ultimate guide for you so that you do not have to Google for hours. This detailed...
Acne vs. Pimples: What’s the Difference?
Home / Blogs / Acne vs. Pimples: What’s the Difference?Acne vs Pimples: What’s the Difference?Reviewed By: Dr. Dhanraj ChavanUpdated on: 17th May, 2025Yet many people aren’t aware that there’s a difference between acne and pimples, and use the two terms...
Home Remedies for Melasma: Natural Solutions for Flawless Skin
Home / Blogs / Home Remedies for MelasmaHome Remedies for Melasma: Natural Solutions for Flawless SkinReviewed By: Dr. Dhanraj ChavanUpdated on: 16th May, 2025Are dark patches on your face affecting your confidence? It could be melasma, a common skin condition...
Effective Skin Lightening Creams for Melasma: What Really Works?
Home / Blogs / Effective Skin Lightening Creams for Melasma: What Really Works?Effective Skin Lightening Creams for Melasma: What Really Works?Reviewed By: Dr. Dhanraj ChavanUpdated on: 30th Apr, 2025 Are you tired of dealing with the frustrating and unsightly...
Why My Acne Is Not Going Away?
Home / Blogs / Why My Acne Is Not Going Away?Why My Acne Is Not Going Away?Reviewed By: Dr. Dhananjay ChavanUpdated on: 28th Apr, 2025 Everyone, regardless of their age or way of life, deals with acne to some extent at some point in life. Many people question why...
Didn’t Find What You Were Looking?Please
Contact Us.
We are committed not only to treating you, but also educating you.
