Skin Pigmentation Treatment in Pune
Your journey to smoother, pigmentation-free skin starts here.
What is Skin Pigmentation?
The natural tone of your skin describes its pigmentation. It is mainly determined by the amount of melanin pigment produced within specialized cells known as melanocytes. Melanin levels differ among individuals and are influenced by genetics, exposure to sunlight, and certain diseases. Despite its critical role in defending against harmful UV rays emitted by the sun, uneven distribution of melanin can cause various skin pigmentation disorders. These disorders can appear as hyperpigmented or hypopigmented conditions, where some parts of the skin become darker while others lose their color completely. Common types of these conditions include vitiligo, melasma, and age spots. Understanding the complexity of skin pigmentation is essential for maintaining health and meeting aesthetic demands.
Several skin pigmentation treatments in Pune are available today to address hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation issues. Advancements in dermatology have made prevention techniques more effective, allowing these disorders to be managed more successfully for even-toned, radiant skin.
| Downtime | Avg Cost Of Treatment | No. Of Sessions Required | Success Rate | No. Of Patients Treated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max 3 Days | Depends On Treatment | 6-8 Sessions | 80% | 80,000+ |
Many Treatments. One Goal.
Best Pigmentation Results In Pune
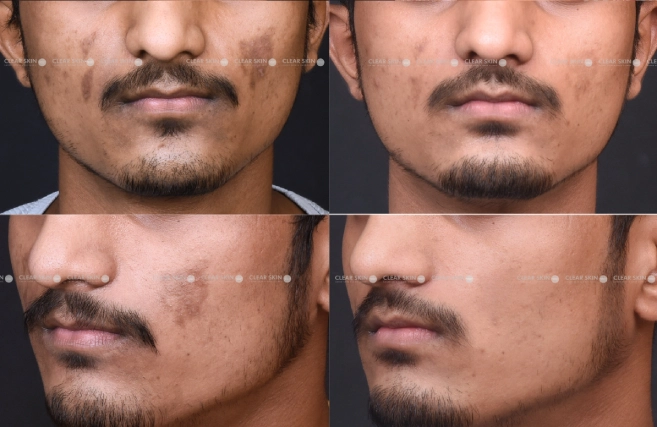
After struggling with uneven skin tone, our patient achieved a brighter and more uniform complexion through our targeted pigmentation treatment in 5 months and 5 sessions.
Conditions
Skin Pigmentation
Treatment
Medications, Laser Therapy, Chemical Peel, Microdermabrasion
Duration
5 Months, 5 Sessions (Settings)
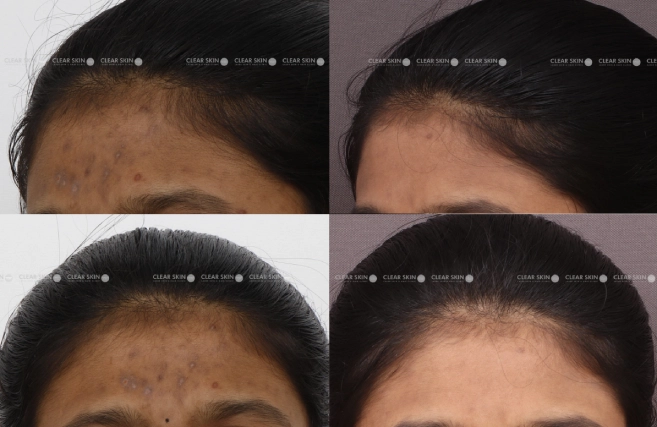
Battling stubborn dark spots, our patient saw a significant improvement in skin clarity with our specialized pigmentation therapy over 4 months and 3 sessions.
Conditions
Skin Pigmentation
Treatment
Medications, Laser Therapy, Chemical Peel,
Duration
4 Months, 3 Sessions (Settings)
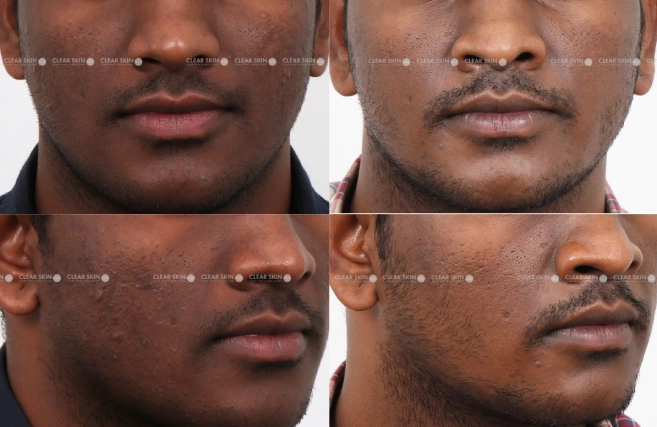
Enduring years of hyperpigmentation, our patient achieved remarkable skin tone uniformity through our comprehensive pigmentation treatment in just 3 months and 3 sessions.
Conditions
Skin Pigmentation
Treatment
Medications, Laser Therapy, Chemical Peel, Microdermabrasion
Duration
3 Months, 3 Sessions (Settings)
With Our Proprietary Treatment Approach, We Have Treated 80000+ Patients Successfully.
Be one of them!
Many Treatments. One Goal.
Yes, It Is Possible To Get
Skin Pigmentation Free Skin.
80,000+ Successfully Treated Skin Pigmentation Patients Over 34+ years
(You are one click away from flawless skin)
All You Need To Know About Skin Pigmentation

Sun Exposure
The sun is one of the main causes of skin pigmentation, especially dark pigmentation. The role of melanin pigment is to protect our cells and DNA from the harmful UV radiation of the A regular use of sunscreens can thus protect one from harmful UV rays plus prevent pigmentation issues.

Hormonal Changes
Hormones are another established cause of pigmentation problems. Many hormonal imbalances are responsible for pigmentation issues like Melasma is a condition which is usually seen post pregnancy, or menopause or due to oral contraceptives.

Skin Inflammation
Inflammatory responses in the skin, caused mainly by conditions such as acne, infections or eczema, lead to skin inflammation. This inflammation results in post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation (PIH). In some cases, our bodies produce excessive melanin as a natural mechanism during the healing process, while in some cases the injury kills melanocytes causing hypopigmentation.
The skin condition where some parts of your skin are darker than others, most common on sun-exposed areas like the face and hands, is hyperpigmentation. These patches appear darker because of the presence of too much melanin in those areas. Factors such as sun exposure, hormonal changes, or skin injuries cause this overproduction, resulting in uneven shades on your skin. Hypopigmentation refers to when some parts of the body have less pigment and appear whiter as compared with surrounding tissues. This kind of disorder may occur throughout the body or be confined to specific areas. Certain infections, injury or autoimmunity are main causes for hypopigmentation.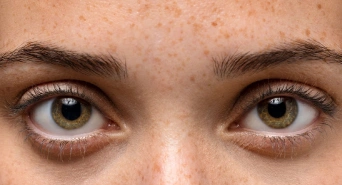
Hyperpigmentation

Hypopigmentation
To lighten hyperpigmented areas, topical creams or gels that contain hydroquinone, retinoids, and vitamin C can be prescribed. Sunscreens are advised as an added benefit to reduce dark pigmentation. For hypopigmentation, creams that stimulate melanin synthesis are usually prescribed which are followed by sun exposure to bring back the pigment. Lasers are used to target pigmented parts of the body. They break down melanin deposits so that they can be excreted naturally by the body. The best dermatologist in Pune uses different types of lasers, such as Q switched laser, to address various pigmentation issues. This approach provides specific and effective treatments tailored to different skin types. When someone undergoes a chemical peel, a solution of active agents is applied on their skin which promotes exfoliation of the skin and removal of pigment through the skin.. The active ingredients used during this process include glycolic acid, salicylic acid, and trichloroacetic acid (TCA). They are responsible for affecting the development of new cells, hence preventing pigmentation scars on our faces.
Topical Treatments

Laser Therapy

Chemical Peels
This type of laser works by targeting the melanin in our skin; it breaks down excessive melanin deposits without interfering with neighbouring tissues. It's good at removing melasma, age spots as well as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Each treatment session requires minor downtime, which takes little time, to achieve the best results from this procedure, you need multiple treatments.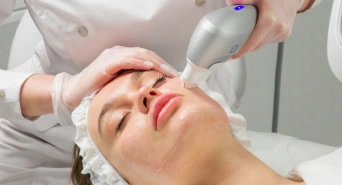
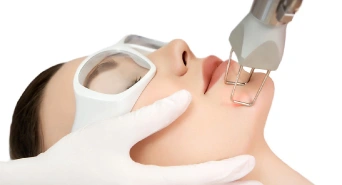
Fractional CO2 Laser
Suppose you see persistent differences in your skin colour of different types, e.g., dark patches, light spots, and any other unusual pigmentation that does not disappear at all; consult top skin specialists in Pune. Early detection assists in curing this condition, hence avoiding progression. Any new mole or changing state among the existing moles, for example, the color alteration, increased size, or reduced size on the body, should lead to immediate intervention by dermatologists. As we know, moles indicate how our skin is doing with time passing by. Those alterations within them could serve as pointers indicating melanoma, thus requiring immediate attention from healthcare providers. Whenever your self image is affected by any pigmentations like melasma, vitiligo, or any other patchy pigmentations consult a professional dermatologist for help. They will advise you regarding that issue in terms of its efficient control.
Continuous Changes in Skin Color
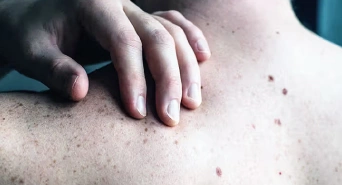
New or Changing Moles

Skin Pigmentation Impacting on Quality of Life
Many Treatments. One Goal.
Our Patients Living Confidently Everyday.
I visit this place for my acne problem and I got excellent result. Dr Sumit is very humbal and kind and give me very effective treatment and all staff is very friendly.
I was going through acne since long...found clear skin hair md and got fantastic result for my acne best clinic for acne prone skin...thank you. Me highly recommend for people who are going through acne 🙂
Professional Acne solutions for all the skin types are available here. Big thanks to Kishori ma’am for helping me out with all my skin related issues, highly recommended.
Clearskin clinic is rated excellent on google & practice
(4.9 out of 5 based on 8289 google & 8000+ practo reviews )
Many Treatments. One Goal.
Clear Skin. We Care.
ANXIOUS ABOUT INCREASING SKIN PIGMENTATION? SEEK HELP FROM THE BEST SKIN PIGMENTATION SOLUTION IN PUNE!
Many customers prefer Clear Skin Clinic for the best treatments for Skin Pigmentation in Pune because it is the most recommended clinic for this issue. Our team of specialized dermatologists at the best pigmentation clinic Pune has extensive experience in treating various forms of skin pigmentation, allowing us to offer unmatched personalized attention to our patients. Additionally, we provide advanced technologies and treatments for skin pigmentation that are safe, effective, and customizable to individual skin types. Thirdly, Clear Skin Clinic Services commits to patient satisfaction and visible results set us apart, making us the reliable choice for countless individuals seeking clearer, healthier skin in Pune.
We
Highly experienced, board-certified, and the best dermatologist in Pune for skin pigmentation leads the team, supported by well-trained medical staff.
Dermatology services in Pune using effective and state-of-the-art technologies and equipment.
Provides personalised skin pigmentation treatment plans and guidance to each patient following a thorough assessment and profiling of their condition.
Actively involved in dermatological research and continually updated with the latest education on skin pigmentation treatment.
Others
Expertise levels can vary among practitioners.
Availability of the latest technology may not be consistent across all clinics.
Treatment approaches may vary widely for different conditions.
Service offerings and patient-centric approaches can vary.
Not constantly updated with the latest advancements.
Hygiene, safety standards, and ethical practices may vary between clinics.
Responsiveness of the Patient Care Team may vary.
We Are Committed Not Only To Treating You,
But Also Educating You.
One Of The
Largest Youtube
Channel
On Skin Care
Follow us to learn the best & authentic know-hows of skin treatments from veteran dermatologist in Maharashtra
Be The Part Of 1,175,644+ Family
Visit Our Channel
Treatments For Hyperpigmentation | Clear Skin, Pune
What Are The Types Of Hyperpigmentation | Clear Skin, Pune
What Is Hyperpigmentation & Causes Of Hyperpigmentation | Clear Skin, Pune
Patient Guides

Best Acne Spot Treatments
Acne spots are marks left behind after acne breakouts, ranging from redness to hyperpigmentation. Find the best treatments for clear skin.
How to Avoid Acne in Monsoons?
Avoid acne in monsoons with a gentle skincare routine, diet tips, and hydration. Get expert advice to manage breakouts and keep your skin clear and healthy.
Does Makeup Cause Acne-Prone Skin?
Worried about breakouts from using makeup? Does makeup cause acne for you? Learn the safe ways to apply makeup for acne-prone skin.
Morning Skin Care Routine for Glowing Skin
Clear Skin Clinic, led by top dermatologists, shares the ideal morning skincare routine to help you achieve a radiant complexion naturally and effectively.
Monsoon Skin Care Tips for Radiant, Healthy Skin
Clear Skin Clinic, led by top dermatologists, shares the ideal morning skincare routine to help you achieve a radiant complexion naturally and effectively.
How To Take Care Of Oily Skin in Monsoon?
Oily skin care in monsoon focuses on gentle cleansing, hydration, and protection to reduce breakouts, greasiness, and help maintain skin balance daily.
Is Laser Hair Removal a Permanent Solution?
Can Laser Treatment Remove Hair Permanently?
We Are Here To Answer Every Possible Doubt You Have On Skin Pigmenation.
If you don’t find answer to your query, then please write down to is. We are always there to help you.
What removes pigmentation from the skin?
You can go for a range of clinical or natural treatment options to remove pigmentation from the skin. While the former includes cryotherapy, dermabrasion, etc., the natural ones can include following a healthy diet, applying a blend of various natural ingredients, and avoiding UV exposure. A detailed consultation with a qualified and experienced dermatologist can help you choose the right treatment.
Which treatment is best for pigmentation?
It could be difficult to deem a particular one as the best treatment for pigmentation on the face. The effectiveness varies from person to person. Some of the most effective treatments include chemical peels, microdermabrasion, laser skin resurfacing, Carbon Peel Laser (CPL) and Intense Pulse Light Therapy (IPL). It is best to have a case-specific consultation and know the best-suited treatment.
How can I remove pigmentation naturally?
“You can remove pigmentation on your face via home remedies with the following ways, based on what suits you.
– Including an adequate amount of vitamin C in the diet
– Applying aloe vera gel
– Applying to green tea extract
– Using tomato paste”
What are the treatments to get rid of pigmentation?
“To get your pigmentation issue resolved, you need to consult your dermatologist who can guide you on what treatment option would work the best for you post analyzing your medical condition. That being said, most treatments aim to help you by
– Stabilizing melanocytes (specialized skin cell that produces melanin)
– Discouraging the production of new melanin
– Removal of excess melanin from the body
As per health experts, relying on a singular option like laser therapy, chemical reel, IPL, etc. isn’t encouraged to combat the pigmentation issue. Instead, a combination of all the above modalities based on the type and factor responsible (for hyperpigmentation) can help you achieve positive results.”
Can pigmentation be removed permanently?
Laser pigmentation removal provides permanent results, as it directly targets the melanin in melanocytes that causes spots on the skin. Once the treatment is done, pigmentation doesn’t usually reoccur.
Which cream is the best for pigmentation?
To know what’s best in your case, you must consult a dermatologist, who will diagnose your case and prescribe the best-suited cream.
How much does it cost for pigmentation treatment in India?
Pigmentation treatment price in India differs from case to case and depends on factors like the complexities involved, area involved, the number of sessions required, etc. However, the average pigmentation treatment cost in India ranges between Rs. 2000 and Rs. 6000.

