Melasma: Complete Guide to Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Reviewed By: ![]() Dr. Dhanraj Chavan
Dr. Dhanraj Chavan
Updated on: 3rd February, 2022
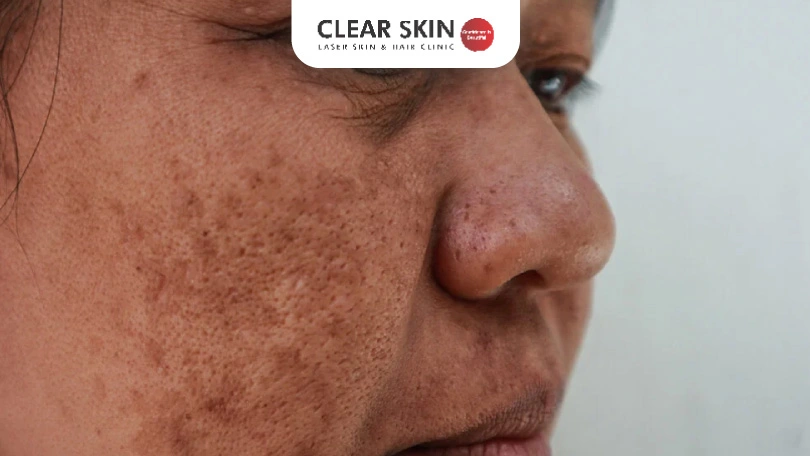
Are you someone who looks in the mirror daily at the brown-grey patches on your face and wonder why me? Have your patches appeared suddenly out of nowhere and worsened with sun exposure?
If so, you may be among the millions worldwide who suffer from melasma. This common yet often-misunderstood skin condition can be frustrating to deal with, but with the right knowledge and medication, it is possible to manage and even improve.
But what exactly is melasma, and why does it affect some people more than others? Are there any treatments that can effectively reduce the appearance of melasma?
In this complete guide to melasma, we will answer all these questions and more. So, let’s explore the world of melasma and discover how to take control of your skin health.
Table Of Content
- What is Melasma?
- Types of Melasma
- Symptoms of Melasma
- Causes of Melasma
- Who is at the Risk of Melasma?
- Diagnosis of Melasma
- Treatment of Melasma
- Prevention of Melasma
- Conclusion
What is Melasma?
Melasma is a skin condition that causes dark, brown coloured patches on the face, especially on the cheeks and nose, in a butterfly-shaped distribution. It may also involve the forehead and upper lip area. It is also known as chloasma or “mask of pregnancy”, as it often affects pregnant women.
Melasma occurs when melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) in the skin produce too much melanin (pigment), and it gets deposited in the skin, causing dark patches. It is more common in women than men and is often triggered by hormonal changes such as pregnancy, birth control pills, or hormone replacement therapy.
Other factors triggering melasma include sun exposure, certain medications, and genetic predisposition.
Melasma is not a dangerous or contagious condition, but it can be unsightly and affect a person’s self-esteem. Melasma is usually diagnosed based on the appearance of the skin, and a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Types of Melasma
Melasma is a common skin condition that causes brown or greyish-brown patches, usually on the face. There are several types of melasma based on the location and pattern of the patches:
Epidermal Melasma
This type of melasma occurs in the upper layer of the skin (epidermis) and appears in brownish patches. It responds well to treatment and is the most common type.
Dermal Melasma
This type of melasma occurs in the deeper layer of the skin (dermis) and appears as bluish-grey patches. It can be difficult to treat and is less common than epidermal melasma.
Mixed Melasma
This type of melasma is a combination of both epidermal and dermal melasma. It appears as a mix of brown and greyish-brown patches on the face and is moderately difficult to treat.
Centrofacial Melasma
Centrofacial melasma usually appears as brown or greyish-brown patches with a well-defined border and is typically symmetrical. Centrofacial melasma occurs in the central part of the face, including the forehead, cheeks, nose, and upper lip.
Mandibular Melasma
Mandibular melasma is a type of melasma that occurs on the lower part of the face, specifically the chin and jawline. It is less common than centrofacial melasma, which affects the central part of the face.
Pregnancy-Related Melasma (Melasma During Pregnancy)
This type of melasma, also known as chloasma, is associated with hormonal changes during pregnancy and appears as brownish patches on the face. It typically goes away after pregnancy but may persist in some cases.
Symptoms of Melasma
Melasma is a common skin condition that usually affects the face and causes brown or greyish-brown patches. The patches are generally symmetrical and can appear on the cheeks, forehead, chin, nose, or upper lip. Some of the common symptoms of melasma include:
Dark Patches on the Skin
The most common symptom of melasma is the appearance of dark, discoloured patches. These patches may be brown, grey, or tan and are usually symmetrical.
Location
Melasma typically appears on the face, particularly on the cheeks, forehead, nose, upper lip, and chin. In rare cases, it can also appear on other body areas, such as the neck and forearms.
Symmetry
Melasma often occurs on both sides of the face and is usually symmetrical.
Darkening with Sun Exposure
Melasma patches may darken with sun exposure, and using sunscreen and avoiding sun exposure can help prevent further darkening.
Causes of Melasma
While the exact cause of melasma is not fully understood, there are several potential risk factors have been identified:
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes in women, such as during pregnancy or while taking birth control pills, can increase the risk of melasma and melasma around the mouth. This is because hormones can stimulate melanin production, which can cause the darkening of the skin.
Sun Exposure
Exposure to the sun can trigger or worsen melasma. This is because UV radiation from the sun stimulates melanin production, and excess melanin can cause dark patches to form.
Genetics
Melasma tends to run in families, suggesting that there may be a genetic component to the condition. However, the specific genes involved have not yet been identified.
Ethnicity
Melasma is more common in people with darker skin tones, such as those of Asian or Middle Eastern descent. This may be because darker skin contains more melanin, making it more susceptible to overproduction and uneven pigment distribution.
Medications
Certain medications, such as hormonal contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy, can trigger melasma in some people. Other medications, such as antibiotics or anti-seizure, have also been associated with the condition.
Cosmetics and Skincare Products
Certain cosmetics and skin care products can irritate the skin and trigger melasma. Products that contain fragrances, as well as some hair dyes, have been associated with the condition.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disease or adrenal gland disorders, can contribute to the development of melasma. These conditions can affect hormone levels in the body, which can, in turn, stimulate excess melanin production.
It is important to note that while these factors contribute to the development of melasma, not everyone exposed to them will develop the condition. Additionally, there may be other factors that are not yet fully understood that can contribute to the development of melasma.
Who is at the Risk of Melasma?
Melasma is more common in women than men and tends to affect individuals with darker skin tones. The following groups of people are at a higher risk of developing melasma:
Women
Although melasma is more common in women, men can also develop this skin condition.
Pregnant Women
Chances of melasma during pregnancy are usually high because of hormonal changes. This is sometimes referred to as the “mask of pregnancy.”
Women on Hormonal Birth Control
Hormonal birth control can also increase the risk of melasma. This is because the estrogen in birth control pills can stimulate the production of melanin, the pigment that gives colour to our skin.
People with Darker Skin Tones
Melasma on nose is more common in individuals with darker skin tones. This is because individuals with darker skin tones have more melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin, and are more prone to hyperpigmentation.
Those with a Family History of Melasma
Melasma tends to run in families, so if you have a close relative who has melasma, you may be more likely to develop it as well.
While these groups may be at a higher risk for melasma, anyone can develop this skin condition. Protecting your skin from the sun and avoiding hormonal triggers can help reduce your risk of developing melasma.
Diagnosis of Melasma
Melasma is typically diagnosed by a healthcare provider specialising in skin disorders, such as a dermatologist. The diagnosis of melasma is primarily based on a visual examination of the affected area, but in some cases, additional tests may be done to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other skin conditions.
During the visual examination, Best dermatologists Pune will closely examine the affected areas of the skin, looking for the characteristic signs of melasma, which are brown or grey-brown patches. The patches are typically symmetrical and appear on the face, particularly on the forehead, cheeks, nose, and upper lip. The dermatologist may use a Wood’s lamp to examine the skin, making the patches more visible and helping determine the pigmentation’s depth.
Sometimes, a skin biopsy may be recommended to rule out other skin conditions that can cause similar symptoms. During a skin biopsy, a small skin sample is taken from the affected area and examined under a microscope to look for signs of other skin conditions.
It is important for patients to provide their complete medical history and any medications they may be taking to help their dermatologist make an accurate diagnosis and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment of Melasma
Melasma is more prevalent in women than men and is often associated with hormonal changes during pregnancy or while taking birth control pills.
The treatment of melasma around mouth and other body areas involves a combination of topical agents, chemical peels, and sometimes laser therapy. It is important to note that treatment can help improve the appearance of melasma.
Topical Agents
Topical agents are usually the first-line treatment for melasma, and they work by inhibiting the production of melanin, which is the pigment that causes dark spots on the skin. Here are some of the commonly used topical agents for melasma treatment:
Hydroquinone
This is the most effective topical agent for melasma treatment. It works by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which is involved in melanin production. Hydroquinone is available in various strengths, ranging from 2% to 4%. It should be used under the guidance of a dermatologist and for a limited period, as prolonged use can cause skin irritation and hypo-pigmentation.
Tretinoin
This derivative of vitamin A is used in combination with hydroquinone to enhance its effectiveness. Tretinoin accelerates skin cell turnover, which helps reduce melasma’s appearance on nose and other areas.
Corticosteroids
These are anti-inflammatory agents that can be combined with hydroquinone and tretinoin to reduce skin irritation and improve the efficacy of the treatment.
Azelaic Acid
This is a natural acid derived from wheat, barley, and rye. It works by inhibiting the production of melanin and reducing inflammation in the skin. Azelaic acid is available in various strengths and formulations, and it can be used alone or in combination with other topical agents. It is usually applied twice daily to the affected area and can take several weeks to see results.
Kojic Acid
This is a natural acid derived from mushrooms and other fungi. It works by inhibiting the production of melanin and reducing inflammation in the skin. Kojic acid is available in various strengths and formulations, and it can be used alone or in combination with other topical agents.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels are a cosmetic procedure that involves the application of a chemical solution to the skin to exfoliate and remove dead skin cells, revealing new, smoother skin. Chemical peels can be an effective treatment for melasma, especially when topical agents are ineffective.
Chemical peels are usually performed in a dermatologist’s office. The procedure takes about 30 minutes to an hour, and it involves the following steps:
- The skin is cleansed and prepared for the peel.
- A chemical solution is applied to the skin and left on for a specific amount of time, depending on the type and strength of the peel.
- The solution is neutralised and removed from the skin.
- A moisturiser and sunscreen are applied to the skin.
Chemical peels can cause some skin redness, stinging, and peeling, which usually subsides within a few days to a week. Patients should avoid sun exposure and use sunscreen to protect the treated area from further damage.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is used for severe cases of melasma that do not respond to topical agents or chemical peels. Laser therapy targets the melanin in the skin and breaks it down. Different types of lasers can be used, such as Q-switched or fractional lasers.
Sun Protection
Protecting the skin from the sun is important in preventing melasma and reducing its severity. This includes wearing protective clothing, using sunscreen with a high SPF, and avoiding direct sunlight during peak hours.
Prevention of Melasma
Preventing melasma can be challenging, as several factors can contribute to its development, including genetics, hormonal changes, and sun exposure. However, there are several steps that individuals can take to reduce their risk of developing melasma or to prevent it from worsening:
- Protect your skin from the sun.
- Avoid tanning beds.
- Be cautious with cosmetic treatments.
- Use gentle skincare products.
- If you are pregnant or considering using hormonal contraceptives, talk to your doctor about ways to manage the risk of developing melasma.
If you have concerns about melasma or are at a higher risk of developing it, talk to your dermatologist about ways to reduce your risk and protect your skin.
Do You Know?
Roughly 250 Patients Are Treated
Everyday By These Dermatologists
(You are one click away from flawless skin)
Meet Our Dermatologist!
Conclusion
Melasma is a common skin condition affecting millions of people worldwide, especially women. It is characterised by dark, discoloured patches on the face and can be triggered by various factors, including sun exposure, hormonal changes, and genetics.
At Clear Skin Clinics in Pune, we understand melasma’s impact on your confidence and quality of life, which is why we offer a range of safe and effective treatments to help you achieve clear, healthy skin. Our experienced dermatologists will work with you to develop a personalised treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and goals.
Don’t let melasma hold you back – contact Clear Skin Clinics, Pune, today to schedule a consultation and take the first step towards achieving clear, beautiful skin.
Further Reading
How to Avoid Acne in Monsoons?
Avoid acne in monsoons with a gentle skincare routine, diet tips, and hydration. Get expert advice to manage breakouts and keep your skin clear and healthy.
Does Makeup Cause Acne-Prone Skin?
Worried about breakouts from using makeup? Does makeup cause acne for you? Learn the safe ways to apply makeup for acne-prone skin.
Morning Skin Care Routine for Glowing Skin
Clear Skin Clinic, led by top dermatologists, shares the ideal morning skincare routine to help you achieve a radiant complexion naturally and effectively.
Monsoon Skin Care Tips for Radiant, Healthy Skin
Clear Skin Clinic, led by top dermatologists, shares the ideal morning skincare routine to help you achieve a radiant complexion naturally and effectively.
Have thoughts? Please let us know
We are committed not only to treating you, but also educating you.





